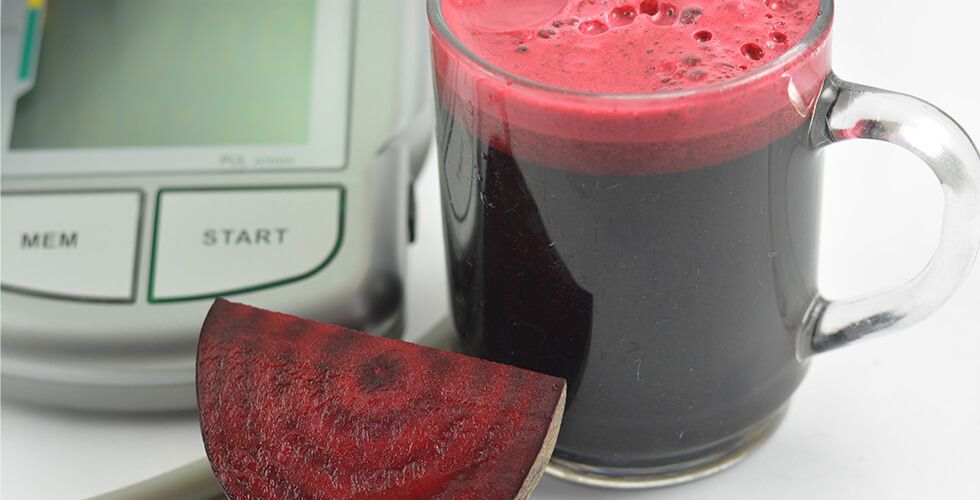
When it comes to managing blood pressure, we often think of exercise, stress management, and medication. But new research suggests that an everyday vegetable—the beet—could play a powerful supporting role in heart health.
A recent study published in Free Radical Biology and Medicine found that older adults who drank nitrate-rich beet juice every day experienced lower blood pressure compared to when they drank a placebo. The key lies in beets’ natural nitrates, compounds that transform into nitric oxide once metabolized by oral bacteria and stomach acids. Nitric oxide helps relax and widen blood vessels, a process known as vasodilation, which lowers blood pressure and improves circulation.
The study followed two groups: young adults and older adults, over multiple phases. Interestingly, the older participants showed the greatest benefit, including shifts in their oral microbiome. Beneficial bacteria like Neisseria increased, while less helpful strains decreased, boosting the conversion of nitrates into heart-friendly nitric oxide.
This isn’t the first time beets have impressed scientists. Prior analyses revealed measurable drops in systolic blood pressure after daily consumption of as little as 70 to 250 milliliters of beet juice. The effect can last for weeks, making beets a simple yet effective dietary tool.
Beyond blood pressure, beets pack other perks: they’re high in fiber for gut health, loaded with antioxidants to fight inflammation, and rich in potassium and folate to support heart function. Nutritionists also note their potential to enhance athletic performance by improving cellular energy production.
How much should you eat? Experts recommend about one cup of beets—or a daily glass of beet juice—for consistent benefits. And if beets aren’t your thing, other nitrate-rich vegetables like spinach, celery, and kale can provide a similar effect.
The takeaway: this humble root may not replace medication, but it can give your heart—and your health—an everyday boost.